Mount Pinatubo 1991
Philippines | VEI 6 | One of the largest 20th century eruptions | How warning systems saved 99,000 lives
VEI 6
Colossal Eruption
~1,000
Deaths
1M+
Displaced
75,000
Evacuated Safely
Physical Setting
- • Luzon Island, Philippines
- • 90km northwest of Manila (capital)
- • Tropical climate with monsoon season
- • Steep-sided stratovolcano
Tectonic Setting
- • Destructive plate boundary
- • Philippine Sea Plate subducting under Eurasian Plate
- • Part of Pacific Ring of Fire
- • Dormant for 500+ years before 1991
Eruption Timeline
March 15, 1991
First Warning Signs
Small earthquakes detected near Pinatubo. Scientists begin monitoring.
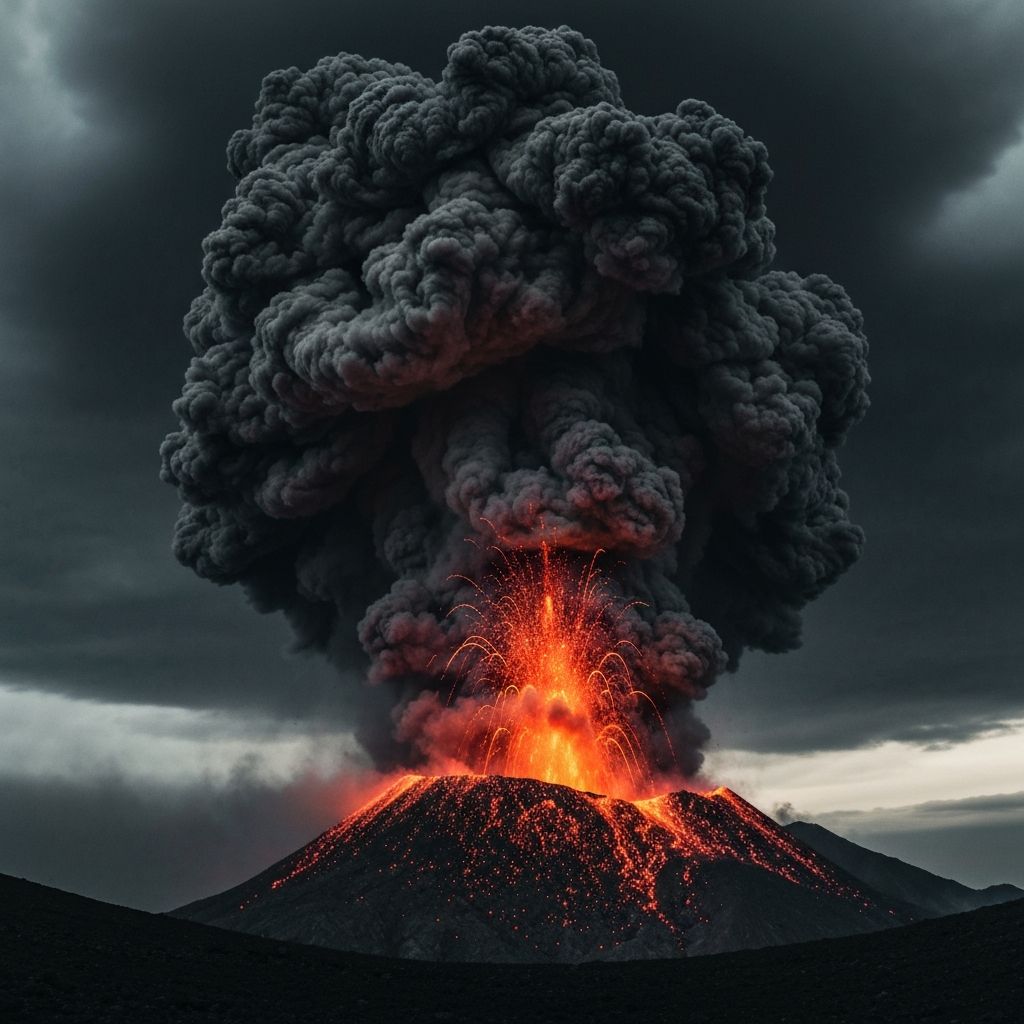

June 15, 1991
Eruption column reached 35km into stratosphere - visible from Manila
Pyroclastic Flows
- • Swept 25-30km from crater
- • Temperature: 700°C
- • Speed: up to 100km/h
- • ~58 immediate deaths
Ash Fall
- • 10 million tons of ash ejected
- • Darkness at noon in Manila (90km away)
- • 4,000+ km² covered
- • Roof collapses from weight
Lahars - The Ongoing Killer
Typhoon Yunya hit the same day as the eruption. Rain mixed with ash created deadly lahars.
- • 1,000 km² flooded with mudflows
- • Continued for 10+ years (every monsoon season)
- • 200+ additional deaths over following decade
- • Rivers blocked → widespread flooding
Agricultural Impact
- • 750,000 hectares farmland damaged
- • 100,000+ livestock killed
- • Crops destroyed by ash and lahars
Economic Damage
- • $250+ million total damage
- • Philippines worst disaster at time
- • Clark Air Base permanently closed
Hazard Zone Mapping
Red zone: 25km pyroclastic flow radius (700°C, instant death)
Blue paths: Lahar routes down river valleys (continued 10+ years)
Gray zone: Ash fall area (4,000+ km² covered)
Immediate (0-72 hours)
- • US military (Clark Air Base) provided evacuation helicopters
- • 75,000 evacuated from 30km danger zone
- • Medical teams deployed for burn victims
- • Search and rescue in accessible areas
Short-term (weeks-months)
- • International humanitarian aid
- • Temporary shelters for 1 million displaced
- • Lahar dams constructed (partially successful)
- • Emergency healthcare for respiratory illness
Long-term (years)
- • Reforestation programs
- • Lahar-resistant infrastructure rebuilt
- • Permanent monitoring systems installed
- • Agricultural rehabilitation
Pinatubo was one of the largest eruptions of the 20th century (VEI 6), yet "only" ~1,000 people died. Compare this to smaller eruptions that killed tens of thousands.
The Key: Early Warning System
- • Scientists detected precursor earthquakes 2 weeks before climax
- • Mass evacuation ordered based on scientific prediction
- • 75,000 evacuated from danger zone before eruption
- • Estimated 99,000 lives saved by warning system
Grade 8/9 Point: Effective monitoring + timely evacuation can prevent mass casualties even from extreme eruptions.
Compare Volcanic Events
Mount Pinatubo 1991
Location
Philippines (LIC)
VEI
6 (Colossal)
Deaths
~1,000
Warning Time
2 weeks
Evacuated
75,000
Key Factor
Early warning system worked
Outcome: 99% of at-risk population saved
Key Learning: Pinatubo was VEI 6 (much larger) but had far fewer deaths than smaller eruptions because warning systems enabled effective evacuation.
Test Your Knowledge
Scientists detect increased earthquake activity under the volcano. What should authorities do FIRST?
Score: 0/4
Exam Practice
Pinatubo erupted with a VEI of 6 - one of the largest eruptions of the 20th century. Yet the death toll was 'only' ~1,000. Compare to other major volcanic disasters and explain why Pinatubo had a relatively low death toll despite extreme magnitude. (6 marks)