Plate Tectonics & Plate Boundaries
Understanding how Earth's plates move and create hazards at boundaries
Key Concepts
The theory that Earth's crust is divided into large rigid plates that float on the semi-molten mantle and move due to convection currents.
Circular movements in the mantle caused by heat from the core. Hot rock rises, cools, then sinks - dragging tectonic plates along.
Earth's Structure
The Earth has three main layers. The thin outer crust (5-70km) is broken into tectonic plates. Below this, the mantle (2,900km thick) is semi-molten rock that flows very slowly.
At the centre is the core - extremely hot (5,000°C+) and made of iron and nickel. Heat from the core creates convection currents in the mantle, which drive plate movement.
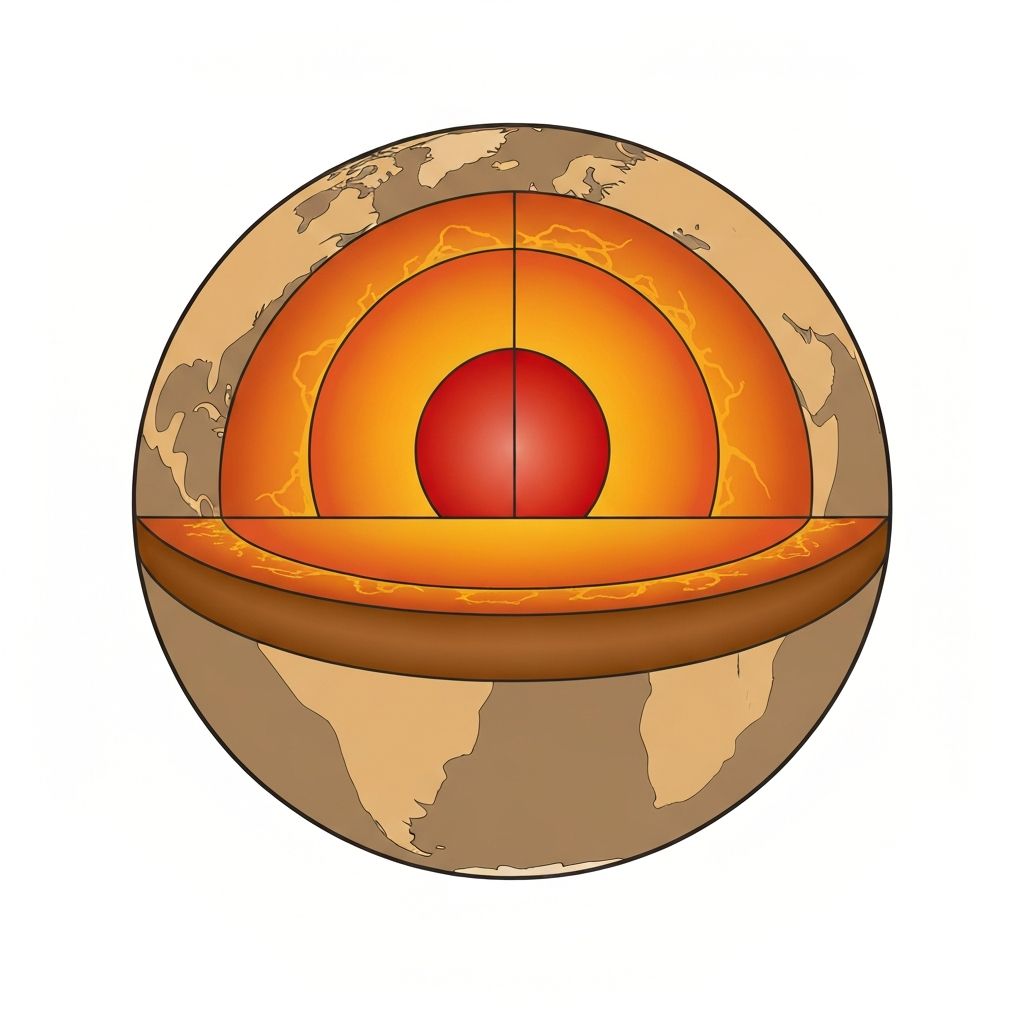
Crust
Thin, solid rock
5-70km thick
Mantle
Semi-molten rock
2,900km thick
Core
Iron & nickel
Very hot center
Three Boundary Types
Click each boundary type to explore the process and hazards produced.
Plate Boundary Explorer
Constructive Boundary
Process
- 1Plates move apart from each other
- 2Magma rises from mantle to fill gap
- 3New oceanic crust forms as magma cools
- 4Creates mid-ocean ridges and rift valleys
Hazards Produced
Earthquakes
Frequent, but LOW magnitude
Volcanoes
Yes - effusive eruptions (runny lava, less dangerous)
Boundary Diagrams
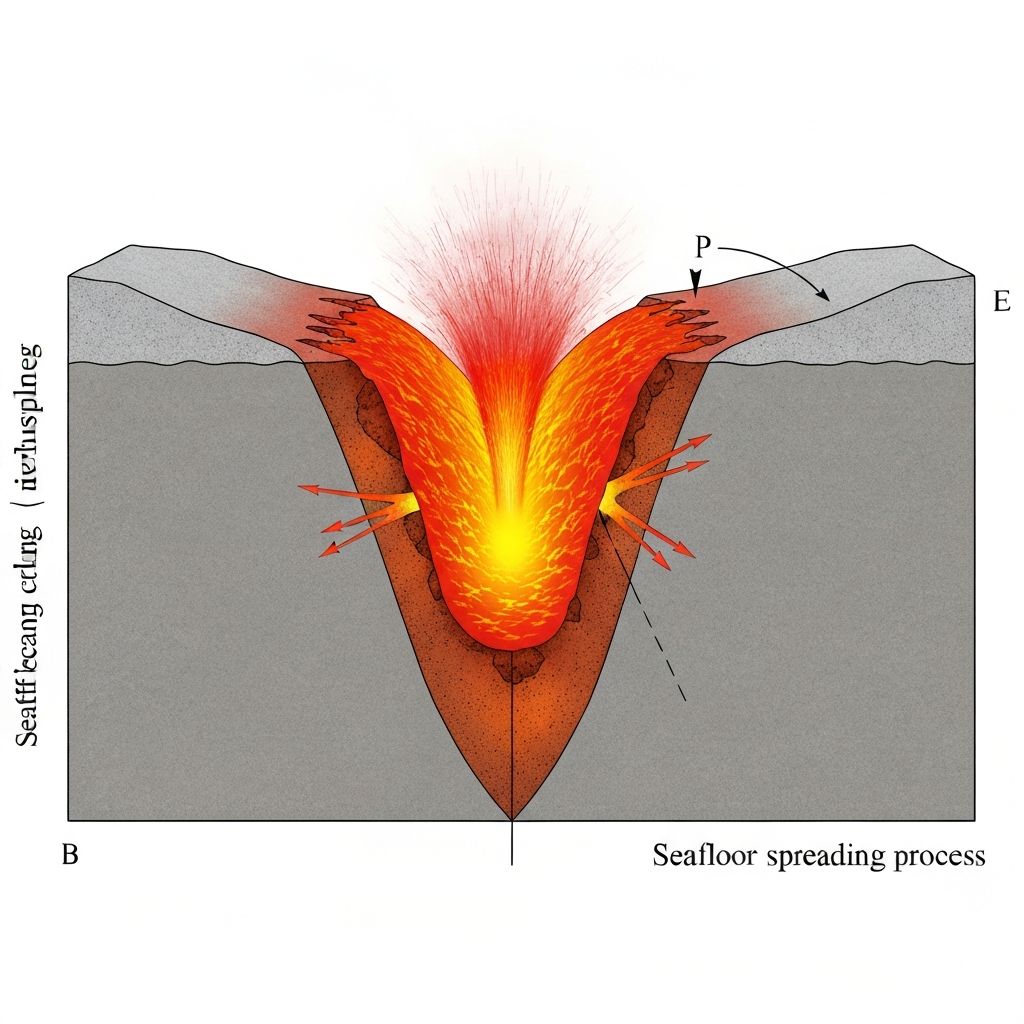
Constructive
Plates apart, magma rises
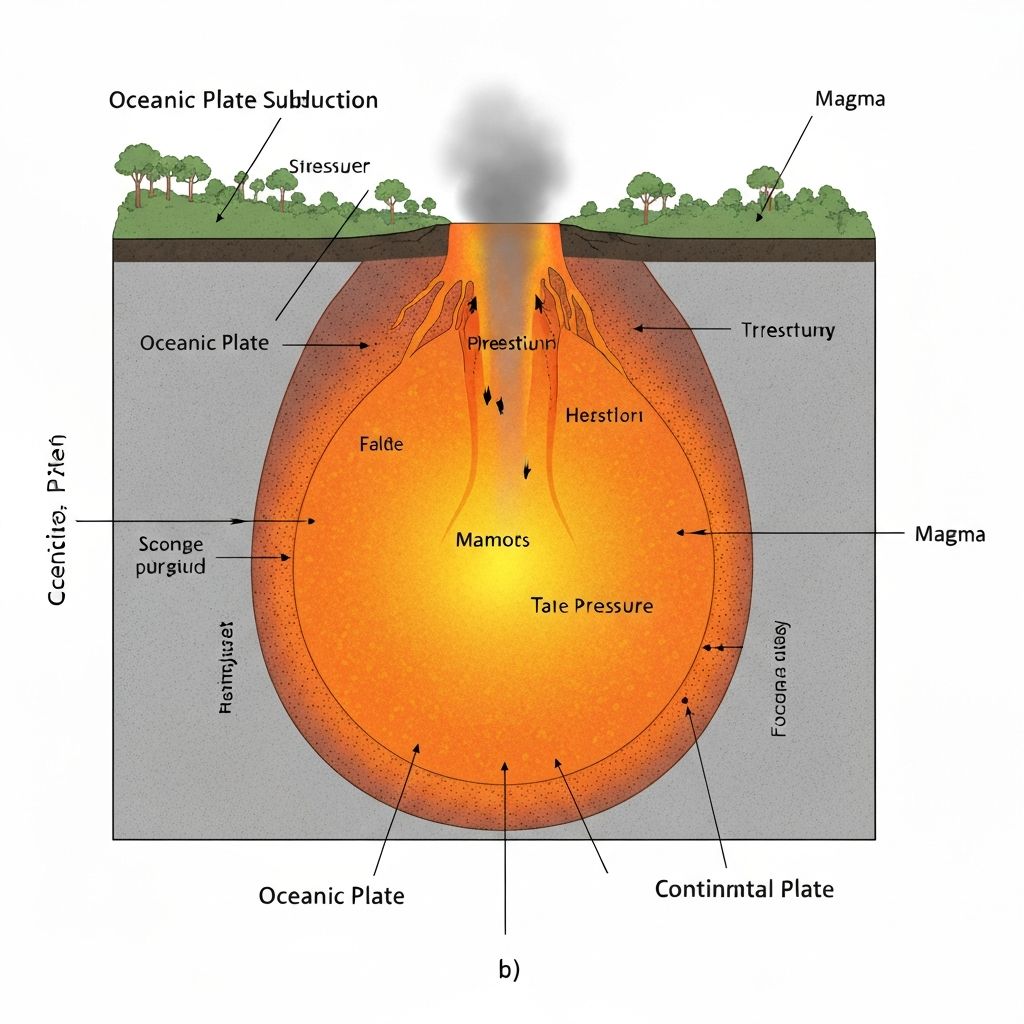
Destructive
Plates collide, subduction
Conservative
Plates slide past
Global Distribution
Ring of Fire
90% earthquakes, 75% volcanoes. Destructive boundaries around Pacific.
Alpine-Himalayan Belt
Major earthquake zone from Europe to Asia. Collision boundaries.
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Underwater constructive boundary. Creates Iceland's volcanoes.
Boundary Comparison
Plate Boundary Types Comparison
| Factor | Constructive | Destructive | Conservative |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plate Movement | Apart (diverging) | Together (converging) | Sideways (sliding) |
| Earthquakes | Frequent, LOW magnitude | HIGH magnitude | HIGH magnitude |
| Volcanoes | Yes - effusive | Yes - explosive | NO volcanoes |
| Landforms | Mid-ocean ridges, rift valleys | Ocean trenches, fold mountains | Fault lines |
| Example | Mid-Atlantic Ridge | Nazca-S.American | San Andreas Fault |
Test Yourself
At which boundary type do plates move apart?
Exam Practice
Two regions experience volcanic eruptions: (1) Japan at a destructive boundary where the Pacific plate subducts under the Eurasian plate; (2) Iceland at a constructive boundary on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Explain why Japan experiences more dangerous volcanic eruptions. [4 marks]
Key Terms Flashcards
Grade 8/9 Tip
Always link boundary TYPE → SPECIFIC HAZARD TYPE → MAGNITUDE. For example: "Destructive boundaries produce high-magnitude earthquakes because the subducting plate sticks then releases suddenly" shows deeper understanding than just listing hazards.